Embarking on a real estate journey in Thailand as a foreign investor offers immense opportunities, but understanding property ownership for foreigners in Thailand is essential. In this guide, we’ll navigate the legal landscape and ownership regulations to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Property Ownership for Foreigners in Thailand
The cornerstone of land ownership regulations in Thailand lies in the 1979 Land Code Act. This pivotal legislation defines the restrictions and eligibility criteria for foreign property buyers, setting the stage for a transparent and regulated property market. It’s imperative for foreign investors to grasp the significance of this act to facilitate a smooth property purchase process.
Legal Restrictions on Property Ownership for Foreigners in Thailand:
As previously mentioned, foreign ownership of land is restricted in Thailand under the provisions of the 1979 Land Code Act. Direct ownership of land by foreigners is prohibited by Thai law. However, various legal mechanisms enable foreigners to indirectly own land, including leasehold agreements, Thai companies, or partnerships with Thai nationals.
Land Ownership Through Thai Companies:
One prevalent method for foreign land ownership involves establishing Thai companies. Foreigners can establish Thai companies in which they hold up to 49% of the company’s shares, allowing them to acquire land indirectly. While this approach is widely accepted and compliant with Thai laws, it entails legal and financial considerations that necessitate consultation with legal experts.
Exploring Property Types Available to Foreigners:
Condominium Ownership for Foreign Investors:
Condominiums emerge as one of the most accessible property options for foreigners in Thailand. Thai law permits foreigners to own condominium units, subject to certain restrictions. Up to 49% of the total floor area in a condominium building can be owned by non-Thais, making condominium ownership a straightforward path for expatriates.
When acquiring a condominium unit, foreigners can directly purchase it, transfer funds from abroad in foreign currency, and ensure compliance with currency exchange laws. Condominium ownership offers several advantages, including the right to sell, rent, or transfer the unit to another foreigner, providing flexibility and investment potential. However, it’s essential to be mindful of monthly maintenance fees associated with condominium ownership and seek legal guidance to navigate the purchase process seamlessly.
Leasehold vs. Freehold Land Ownership:
While condominiums offer a viable option, some investors may seek larger properties such as land or houses. In such cases, foreigners typically opt for either leasehold or freehold land ownership.
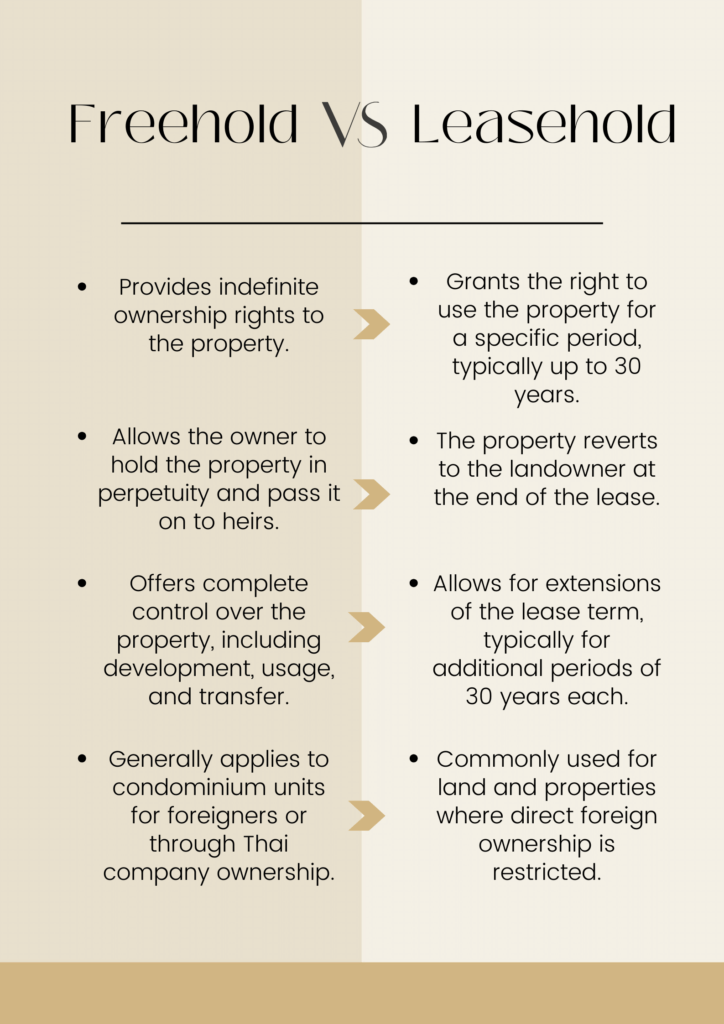
Leasehold Land Ownership:
Foreigners can enter long-term lease agreements for land, typically lasting 30 years with options for renewal. These leases grant a degree of security and control over the property during the lease period. However, it’s crucial to thoroughly understand the lease duration, renewal terms, and conduct due diligence on the property and lease agreement before finalizing the transaction.
Freehold Land Ownership:
Direct freehold ownership of land is more restrictive for foreigners due to Thai law prohibiting direct land ownership. However, establishing a Thai company where the foreign investor holds the majority of shares enables indirect ownership of land. This method requires careful consideration of legal and financial aspects, emphasizing the importance of legal expertise to navigate Thai property laws securely.
Conducting Due Diligence and Seeking Legal Assistance:
Before proceeding with a property purchase, conducting thorough due diligence on the property, seller, and legal requirements is paramount. Enlisting the assistance of legal experts or reputable real estate agents can guide investors through the legal process, ensure proper documentation, and negotiate favorable terms. Comprehensive documentation verification safeguards the buyer’s investment and mitigates potential risks associated with property transactions.
Navigating Financing and Tax Considerations:
Foreign investors exploring property ownership in Thailand can explore various financing options, including personal funds, mortgages, or loans. Understanding the financial implications and obligations, including property transfer fees, stamp duty, and income tax, is essential for accurate budgeting. Additionally, considering currency exchange rates when transferring funds into Thailand for property purchase is crucial to mitigate exchange rate fluctuations’ impact on the property’s cost. For the latest exchange rates, check XE.com before transferring funds for property purchases
In conclusion, owning property in Thailand as a foreigner presents viable opportunities within a regulated legal framework. Understanding the available property types, legal regulations, and seeking professional guidance are essential steps for a successful property purchase journey. Whether opting for condominiums, leasehold agreements, or exploring avenues for freehold ownership through Thai companies, responsible property ownership contributes to a vibrant and enduring real estate market in the Land of Smiles. With careful consideration and expert guidance, foreign investors can navigate the complexities of Thai property laws and embark on a rewarding property ownership experience in Thailand.






